1 北京邮电大学理学院,北京 100876
2 陆军装备部驻上海地区航空军事代表室,上海 200233
3 山东中新铝基新材料有限公司,淄博 255000
α-Al2O3在耐火材料、电子材料等多个领域有着极其重要的应用。本文首先介绍了α-Al2O3在工业应用方面的评价指标和α-Al2O3的相变机理,接着分别从固相合成、液相合成、气相合成三个方面阐述了α-Al2O3制备的相关研究进展,对制备过程中影响α-Al2O3晶粒微观状态的若干因素,包括煅烧温度、矿化剂类型、pH值及预处理条件等进行讨论。最后指出了当前对α-A12O3成核生长机理研究缺乏的问题,表明明确的成核机理、高纯度α-A12O3的量产和形貌控制技术将会是该领域未来的研究重点和发展方向。
相变机理 微观形貌 晶粒尺寸 煅烧温度 矿化剂 α-Al2O3 α-Al2O3 transition mechanism micromorphology particle size calcination temperature mineralizer
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, School of Science, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, Shijiazhuang 050043, China
3 School of Science, Minzu University of China, Beijing 100081, China
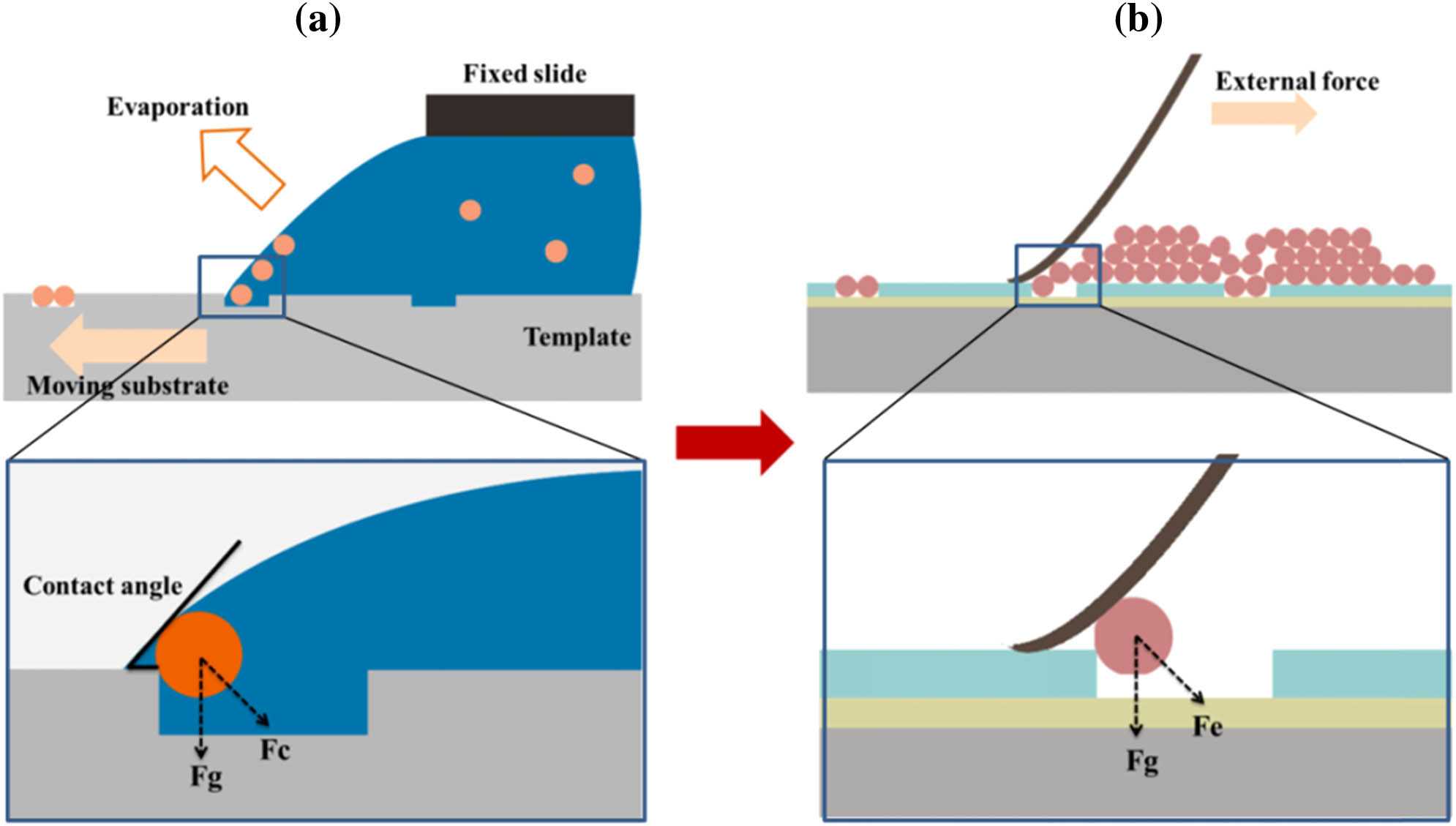
All-dielectric metamaterials have emerged as a promising platform for low-loss and highly efficient terahertz devices. However, existing fabrication methods have difficulty in achieving a good balance between precision and cost. Here, inspired by the nano-template-assisted self-assembly method, we develop a micro-template-assisted self-assembly (MTAS) method to prepare large-scale, high-precision, and flexible ceramic microsphere all-dielectric metamaterials with an area exceeding 900 cm×900 cm. Free from organic solvents, vacuum, and complex equipment, the MTAS method ensures low-cost and environmentally friendly fabrication. The ceramic microsphere resonators can be readily assembled into nearly arbitrary arrangements and complex aggregates, such as dimers, trimers, quadrumers, and chains. Finally, using the heat-shrinkable substrate and dipole coupling effect, a broadband reflector with a bandwidth of 0.15 THz and a reflection of up to 95% is demonstrated. This work provides a versatile and powerful platform for terahertz all-dielectric metamaterials, with potential to be applied in a wide variety of high-efficiency terahertz devices.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(4): 04000457

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Applied Physics, Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, Baotou 014010, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications & School of Science, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
3 State Key Laboratory of New Ceramics and Fine Processing, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
When a dielectric meta-atom is placed into a subwavelength metallic aperture, 20-fold enhanced electromagnetic transmission through the aperture is realized at the meta-atom’s resonant frequency. Additionally, when the incident electromagnetic power increases, thermal energy gathered by the meta-atom, which is converted from electromagnetic losses, can cause the meta-atom’s temperature to increase. Because of the high temperature coefficient of the meta-atom’s resonant frequency, this temperature increase causes a blueshift in the transmission peak. Therefore, this frequency-dependent enhanced electromagnetic transmission even produces a nonlinear effect at low incident powers. Over an incident power range from 0 to 20 dBm, measured and simulated spectra near the meta-atom’s resonant frequency show distinctly nonlinear transmission.
Photonics Research
2018, 6(12): 12001102
1 集成光电子国家重点实验室, 吉林大学电子科学与工程学院, 吉林 长春130012
2 空军航空大学军事仿真技术研究所, 吉林 长春130022
3 超硬材料国家重点实验室, 吉林大学物理学院, 吉林 长春130012
ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS量子点是一种无毒, 无重金属的“绿色”半导体纳米材料。 在研究中, 制备了三种尺寸的ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS核壳量子点, 其直径分别为3.3, 2.7, 2.3 nm。 通过测量不同尺寸的ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS量子点的光致发光光谱, 其发射峰值波长随尺寸的减小而蓝移。 其吸收峰值波长和发射峰值波长分别是510, 611(3.3 nm), 483, 583(2.7 nm)以及447, 545 nm(2.3 nm)。 ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS量子点具有显著的尺寸依赖效应。 ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS量子点的斯托克斯位移分别为398 meV(3.3 nm), 436 meV(2.7 nm)以及498 meV(2.3 nm), 这样大的斯托克斯位移证明, ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS量子点的发光机制与缺陷能级有关。 同时, 对直径为3.3 nm的ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS量子点进行了温度依赖的光致发光光谱的测量, 当温度为15~90 ℃时, 该量子点发射峰值波长随温度的升高而红移, 发光强度随温度的升高而降低, 说明ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS量子点是以导带能级与缺陷能级之间跃迁为主的复合发光。
量子点 温度依赖 尺寸依赖 光致发光光谱 ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS Quantum dots Temperature-dependent Size-dependent Photoluminescence
1 吉林大学物理学院, 超硬材料国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130012
2 吉林大学电子科学与工程学院, 集成光电子国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130012
ZnCuInS/ZnS量子点是一种无重金属“绿色”半导体纳米材料。制备出了直径为2.9 nm的ZnCuInS/ZnS核壳量子点。从ZnCuInS/ZnS量子点的吸收及光致发光光谱中可以看到, 量子点的斯托克斯位移为410 meV。这样大的斯托克斯位移表明, ZnCuInS/ZnS量子点的复合机制与缺陷能级有关。研究并计算了在辐射及非辐射驰豫过程的(Huang-Rhys)因子及平均声子能量。结果表明在50~373 K范围内, 能量带隙的变化以及光致发光光谱的增宽是分别由光从能带边缘向缺陷能级跃迁及载流子声子耦合导致的。
ZnCuInS/ZnS量子点 光致发光 温度特性 能量带隙 ZnCuInS/ZnS quantum dots photoluminescence temperature-dependence energy band gap





